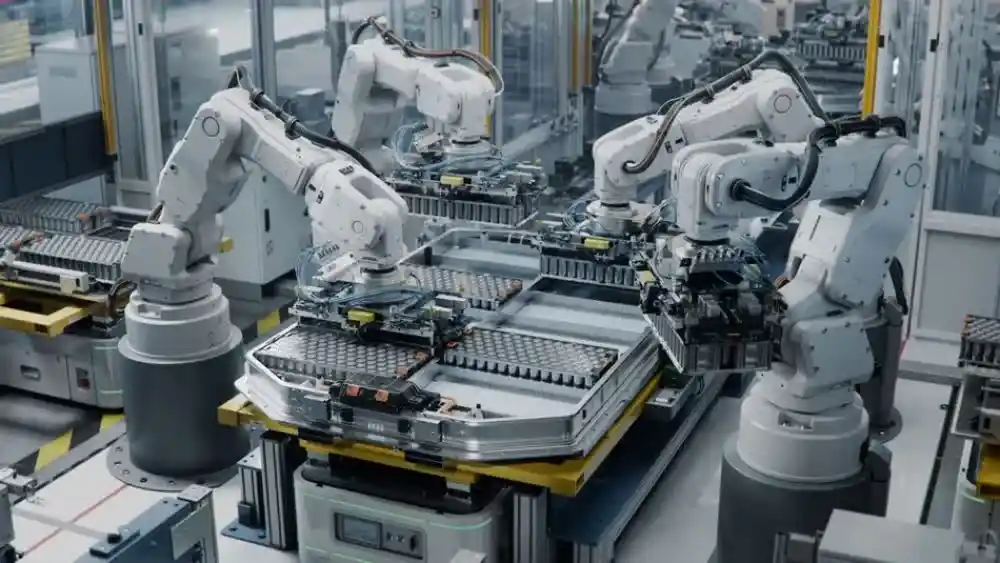
The chemical processing industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the growing need for precision, efficiency, safety, and sustainability. At the heart of this transformation is automation — a powerful force that is reshaping how chemical plants operate. Automation is no longer a luxury or a futuristic concept; it’s a necessity for competitiveness in today’s global market.
In this article, we’ll explore how automation is playing a vital role in modern chemical processing, its benefits, key technologies, and the challenges that companies face in implementing automated systems.
1. Understanding Automation in Chemical Processing
Automation in chemical processing involves using advanced technologies and control systems to monitor and operate equipment with minimal human intervention. This includes everything from sensors and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI).
The goal is to create systems that can perform repetitive, complex, or hazardous tasks accurately and consistently, freeing up human workers for more strategic roles.
2. Key Components of Automation Systems
Modern chemical plants leverage a variety of automation tools to improve efficiency:
- Sensors and Actuators: These are the eyes and arms of automated systems. Sensors detect changes in temperature, pressure, flow rates, and chemical concentrations, while actuators perform actions like opening valves or adjusting mixers.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): PLCs execute predefined logic to control machinery and processes based on sensor inputs.
- Distributed Control Systems (DCS): DCS offer centralized monitoring and control of plant operations, allowing operators to manage everything from a single interface.
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA): SCADA systems provide real-time data visualization and control, often used in conjunction with DCS.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML): These tools analyze vast amounts of data to predict equipment failures, optimize chemical reactions, and improve decision-making.
3. Benefits of Automation in Chemical Processing
Automation delivers numerous advantages that significantly impact plant performance and profitability:
a. Enhanced Efficiency
Automated systems can operate 24/7 without fatigue, ensuring consistent production and minimizing downtime. They also streamline workflows by eliminating manual steps and optimizing process variables in real-time.
b. Improved Safety
Chemical plants are inherently hazardous environments. Automation reduces human exposure to dangerous chemicals, high temperatures, and high-pressure systems, minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
c. Higher Precision and Quality Control
Automation ensures accurate dosing, mixing, and timing, leading to better product consistency and reduced waste. It also allows for real-time monitoring, enabling rapid detection and correction of deviations.
d. Cost Savings
Although automation requires upfront investment, it leads to long-term savings through reduced labor costs, increased throughput, lower material waste, and fewer accidents.
e. Data-Driven Decision Making
Automated systems collect vast amounts of data that can be analyzed for trends and insights. This helps plant managers make informed decisions and continuously improve processes.
4. Applications of Automation in Chemical Processing
Automation plays a crucial role across various aspects of chemical processing:
- Batch Processing: Automated batch control systems manage recipe execution, timing, and sequencing for consistent product quality.
- Continuous Processing: In continuous operations, automation maintains optimal flow rates and reaction conditions, boosting productivity.
- Utilities Management: Automated control of boilers, chillers, and compressed air systems helps reduce energy consumption.
- Inventory and Material Handling: Robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) handle raw materials and finished products efficiently.
- Environmental Monitoring: Automation ensures compliance with environmental regulations by continuously monitoring emissions and effluents.
5. Challenges in Implementing Automation
Despite the many benefits, there are challenges that companies must navigate when integrating automation into chemical processing:
- High Initial Investment: Automation systems require significant capital, which may be a barrier for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- Skill Gaps: Operating and maintaining automated systems requires specialized knowledge. Workforce training and upskilling are essential.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many chemical plants operate with outdated equipment, which may not be compatible with modern automation technologies.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As operations become more connected, protecting control systems from cyber threats becomes critical.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new technologies due to fear of job loss or unfamiliarity.
6. Future Trends in Automation
The automation landscape continues to evolve, offering exciting opportunities for the chemical industry:
- Digital Twins: Virtual models of chemical plants that simulate real-time operations for predictive maintenance and optimization.
- Edge Computing: Real-time data processing at the source to reduce latency and improve responsiveness.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): A network of connected devices that enhance data collection and communication across the plant.
- Cloud Integration: Cloud platforms enable remote monitoring, collaboration, and data storage.
- Green Automation: Focused on sustainability, green automation reduces energy usage and environmental impact through smart control systems.
Automation is revolutionizing the chemical processing industry, driving efficiency, safety, and innovation. From controlling complex reactions to minimizing environmental impact, automated systems are central to modern plant operations.
However, successful implementation requires careful planning, investment, and a willingness to adapt. By embracing automation, chemical companies can position themselves for long-term success in a competitive and fast-evolving marketplace.
As technology continues to advance, the role of automation in chemical processing will only grow more significant — turning challenges into opportunities and unlocking new levels of performance.





Leave a Reply