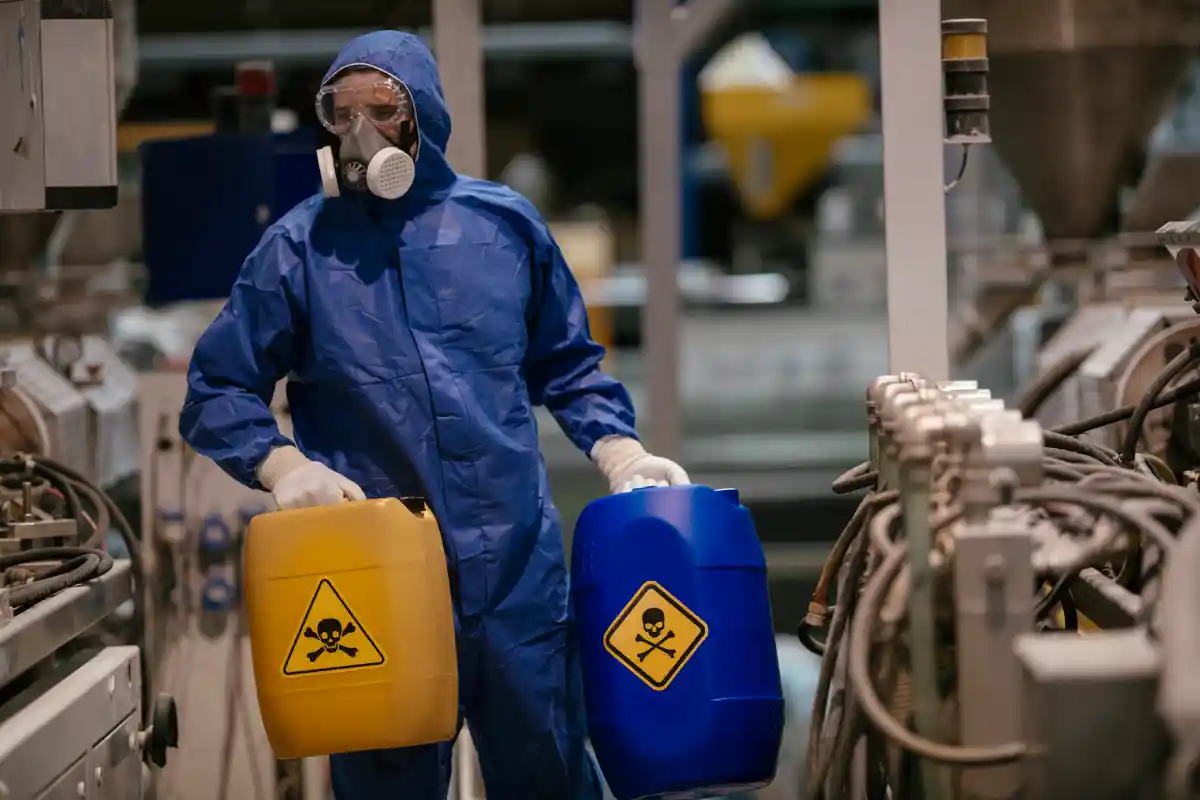

Handling hazardous chemicals is an integral part of many industrial and laboratory operations. These substances, while essential for various processes, pose significant risks to human health, safety, and the environment. Accidental exposure, spills, or improper storage of hazardous chemicals can lead to severe consequences, including injuries, environmental damage, and regulatory penalties. Therefore, managing these materials requires strict protocols, specialized training, and robust safety measures.
In this article, we’ll explore the major challenges associated with hazardous chemical handling and offer practical solutions to ensure safer practices across chemical industries.
Understanding Hazardous Chemicals
Hazardous chemicals include any substances that pose physical, health, or environmental risks. They can be classified into several categories:
- Flammable or combustible: e.g., acetone, ethanol
- Corrosive: e.g., sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide
- Toxic: e.g., cyanide, benzene
- Reactive: e.g., sodium metal, peroxides
- Carcinogenic or mutagenic: e.g., formaldehyde, asbestos
These substances are often vital to manufacturing, research, or cleaning processes, making it impossible to eliminate them entirely. However, the risks associated with their use can be managed effectively.
Key Challenges in Hazardous Chemical Handling
1. Lack of Proper Training
Many accidents occur due to workers not being adequately trained to handle hazardous materials. Without knowledge of proper procedures, risks increase significantly.
2. Inadequate Storage and Labeling
Improperly stored chemicals or mislabeled containers can lead to dangerous mix-ups, accidental exposure, or chemical reactions.
3. Poor Ventilation and Facility Design
Inadequate airflow and poorly designed workspaces can increase the concentration of harmful vapors, posing respiratory and explosion hazards.
4. Spills and Leaks
Even minor leaks can result in long-term exposure, contamination, and environmental damage if not managed promptly and effectively.
5. Improper Waste Disposal
Disposing of hazardous chemicals without following legal or environmental guidelines can lead to severe fines, environmental damage, and harm to public health.
6. Limited Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Failure to use or properly maintain PPE such as gloves, goggles, and respirators increases the likelihood of exposure.
Practical Solutions to Improve Safety
1. Comprehensive Training Programs
Ensure all employees handling hazardous chemicals receive detailed training that includes:
- Identifying chemical hazards
- Using Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
- Emergency procedures (e.g., spill cleanup, fire response)
- Proper use of PPE
Training should be refreshed regularly and tailored to specific job roles.
2. Clear Labeling and Signage
- Label every container with the chemical name, hazard symbols, and handling instructions.
- Use standardized labeling systems like GHS (Globally Harmonized System).
- Post clear signage in storage areas and near equipment.
3. Appropriate Storage Practices
- Store chemicals according to their compatibility. For example, acids should be stored separately from bases and flammables.
- Use ventilated cabinets for volatile substances.
- Maintain an up-to-date inventory to prevent overstocking or expired chemicals.
4. Facility Upgrades and Ventilation
- Install proper ventilation systems like fume hoods and exhaust fans.
- Design workspaces to minimize clutter and facilitate easy access to safety equipment.
- Use explosion-proof storage and electrical systems where necessary.
5. Spill Response Plans
- Equip work areas with spill kits suitable for the chemicals in use.
- Designate spill response teams and conduct regular drills.
- Train workers to contain, clean up, and report spills immediately.
6. Safe Waste Management
- Segregate hazardous waste according to chemical type.
- Use approved containers and disposal services.
- Keep detailed records to comply with local and international regulations.
7. Effective Use of PPE
- Provide PPE suited to the specific chemical hazards.
- Conduct regular checks to ensure equipment is in good condition.
- Train staff on correct donning, doffing, and disposal techniques.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Various agencies set guidelines and standards for the safe handling of hazardous chemicals. Adhering to these not only reduces risks but also ensures legal compliance.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Provides standards like the Hazard Communication Standard (HCS).
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): Regulates chemical waste disposal.
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association): Offers fire safety codes related to chemicals.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals – EU): Ensures chemicals are safely managed in the European Union.
Companies should stay updated on relevant regulations and conduct regular audits to assess compliance.
Case Study: Improving Safety at a Manufacturing Plant
A chemical manufacturing plant in Texas experienced repeated incidents due to improper handling of sulfuric acid. The company invested in a comprehensive safety overhaul:
- Installed dedicated acid storage cabinets with secondary containment.
- Upgraded PPE requirements for all personnel.
- Conducted monthly safety drills.
- Introduced digital checklists for routine inspections.
Within a year, the number of safety incidents dropped by 75%, demonstrating the tangible benefits of proactive safety management.
Future Outlook: Technology and Innovation
Emerging technologies are offering new ways to improve chemical handling safety:
- IoT Sensors: Detect leaks and monitor environmental conditions in real-time.
- Automated Dispensing Systems: Reduce human contact with chemicals.
- Digital SDS Management Tools: Improve access to vital safety information.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Used in training programs to simulate emergency scenarios.
As these technologies become more accessible, they will play a crucial role in minimizing human error and enhancing safety.
Handling hazardous chemicals comes with inherent risks, but these can be managed through proper training, facility design, protective equipment, and strict adherence to safety protocols. Organizations that invest in these areas not only protect their workers and the environment but also enhance their operational efficiency and compliance.
As technology continues to evolve, new tools and innovations will further streamline hazardous chemical management, making chemical handling safer and more sustainable in the years to come.






Leave a Reply