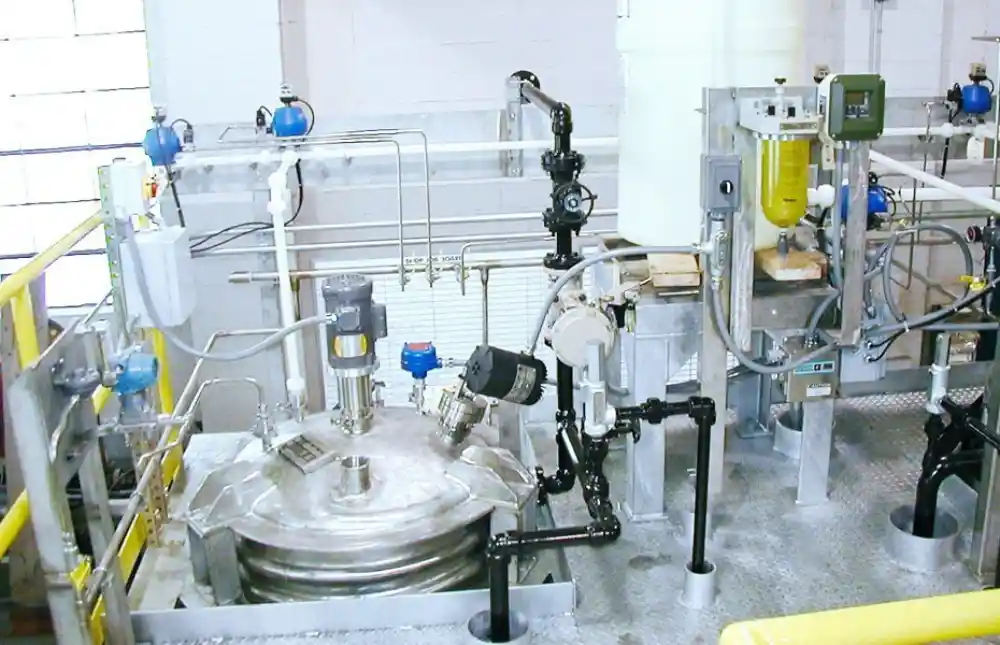

Chemical process control systems are at the heart of modern chemical manufacturing. They ensure that operations run smoothly, safely, and efficiently. As technology continues to evolve, new trends are emerging that are transforming how these control systems operate. From smart sensors to artificial intelligence, these innovations are improving process reliability, increasing productivity, and enhancing sustainability.
This article explores the emerging trends in chemical process control systems and their impact on the industry.
What Are Chemical Process Control Systems?
Chemical process control systems are technologies and strategies used to monitor and regulate chemical production. They maintain optimal conditions such as temperature, pressure, flow, and composition within reactors and processing units. The goal is to produce high-quality products consistently while minimizing waste, energy usage, and environmental impact.
Traditionally, process control relied heavily on manual oversight and simple feedback loops. However, with the rise of digital technologies, modern systems have become highly automated and data-driven.
1. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
One of the most significant trends in chemical process control is the adoption of AI and ML. These technologies enable systems to analyze vast amounts of data, learn from patterns, and make predictive decisions.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can forecast equipment failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Process Optimization: ML algorithms continuously learn from operational data to adjust control parameters for maximum efficiency and yield.
- Fault Detection: AI can detect anomalies in real-time, alerting operators to potential issues before they escalate.
The use of AI is shifting process control from reactive to proactive, leading to more reliable and cost-effective operations.
2. Advanced Process Control (APC)
Advanced Process Control systems go beyond traditional control methods by using mathematical models and algorithms to manage complex processes.
- Model Predictive Control (MPC) is one of the most widely used APC techniques. It uses dynamic models to predict future behavior and adjusts controls accordingly.
- APC improves product consistency, reduces energy usage, and enhances responsiveness to disturbances.
Many chemical plants are integrating APC to improve performance, especially in processes with long delay times or multiple interacting variables.
3. Real-Time Data Analytics
With the proliferation of sensors and connectivity, chemical plants now have access to real-time data streams. This data is analyzed instantly to provide insights that drive decision-making.
- Digital Dashboards: Operators can monitor processes from a central location, receiving visual updates and alerts.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Real-time tracking of KPIs helps maintain targets and quickly address deviations.
- Big Data Integration: Combining real-time data with historical data enhances forecasting and troubleshooting capabilities.
Real-time analytics make process control more responsive and informed, allowing companies to optimize performance continuously.
4. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The IIoT connects devices, sensors, and systems across a facility, enabling seamless communication and data sharing.
- Smart Sensors: These devices monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and chemical composition with high precision.
- Remote Monitoring: Engineers can access system data remotely, improving flexibility and reducing the need for on-site presence.
- Automated Alerts: IIoT systems can send notifications when thresholds are exceeded or anomalies are detected.
By integrating IIoT, chemical plants gain improved visibility and control over their operations.
5. Cybersecurity in Control Systems
As control systems become more connected, they also become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Cybersecurity is now a top priority in chemical process control.
- Firewalls and Encryption: Protecting data transmissions from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Limiting system access to authorized personnel only.
- Security Audits and Updates: Regular assessments and updates ensure systems remain secure.
A secure control environment is critical to maintaining safety and compliance in the chemical industry.
6. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical process or system. It uses real-time data to simulate operations, test scenarios, and optimize performance.
- Process Simulation: Engineers can test changes in the digital environment before implementing them on the plant floor.
- Predictive Analysis: Digital twins help forecast outcomes and assess risks.
- Training and Troubleshooting: Operators can practice procedures or identify issues using the virtual model.
Digital twins enhance decision-making and reduce trial-and-error in process control adjustments.
7. Cloud-Based Control Solutions
Cloud computing offers scalable, cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and analytics.
- Data Accessibility: Teams across different locations can access and collaborate on the same data sets.
- Backup and Recovery: Cloud systems offer reliable backup and fast disaster recovery options.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Control software can be updated automatically and managed remotely.
Cloud technology supports more agile and collaborative chemical process operations.
Challenges and Considerations
While these emerging trends offer significant advantages, they also come with challenges:
- Initial Investment: Upgrading control systems can require substantial capital.
- Workforce Training: Staff must be trained to operate and maintain new technologies.
- Data Management: Handling large volumes of data requires robust infrastructure and policies.
- Change Management: Adoption of new systems may face resistance from personnel accustomed to legacy methods.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and a commitment to continuous improvement.
The field of chemical process control is undergoing a digital revolution. Emerging trends such as AI, IIoT, digital twins, and real-time analytics are transforming how chemical plants operate. These technologies are not only improving efficiency and safety but also supporting sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
As more companies embrace these innovations, staying ahead of the curve will be essential for maintaining competitiveness in the chemical industry. Investing in modern control systems today is a step toward a smarter, more responsive, and more sustainable future in chemical processing.






Leave a Reply